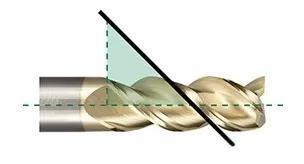
While many factors affect machining outcomes, the helix angle of milling cutters remains a frequently underestimated parameter. Defined as the angle between the tool centerline and a tangent line to the cutting edge, this critical feature directly impacts:
-
Chip evacuation efficiency
-
Surface finish quality
-
Tool lifespan
-
Machining cycle time
Helix Angle Classification
-
Low Helix Angles (<40°)
-
Typical applications: Heavy material removal
-
-
High Helix Angles (>40°)
-
Typical applications: Precision finishing

Milling cutter helix angle
-
Fundamental Principle
As helix angle increases, the engaged cutting edge length decreases. Both extremes (<40° and >40°) present unique trade-offs:
Low Helix Angle Tools (<40°)
✅ Advantages
-
Enhanced Structural Integrity
-
Larger core diameter resists bending deformation
-
-
Workpiece Stability
-
Reduced radial forces minimize workpiece displacement risks
-
-
Aggressive Material Removal
-
Generates larger chips for rapid bulk cutting
-
❌ Disadvantages
-
Suboptimal Surface Finish
-
Chip evacuation challenges cause surface irregularities
-
-
Feed Rate Limitations
-
-
High radial forces necessitate slower feed rates
-

-
High Helix Angle Tools (>40°)
✅ Advantages
-
Superior Cutting Stability
-
Enhanced shearing action reduces vibration (particularly critical for thin-wall machining)
-
-
Effective Chip Management
-
Increased axial forces promote rapid chip removal
-
-
Precision Surface Quality
-
Reduced radial forces enable clean material separation
-
❌ Disadvantages
-
Reduced Cutting Edge Durability
-
Thinner tool geometry increases wear susceptibility
-
-
Deflection Sensitivity
-
Flexible teeth require strict parameter control
-
-
Catastrophic Failure Risks
-
-
Uncontrolled deflection may cause tool breakage
-

-
Key Considerations for Tool Selection
When choosing a milling tool, evaluate:
-
Material properties (hardness, ductility)
-
Operation type (roughing vs. finishing)
-
Machine rigidity (to counteract deflection risks)
-
Chip load requirements (linked to helix angle effects)